Git and GitHub Commands Guide for Beginners Step-by-Step with Examples
Git and GitHub Introduction
Git and GitHub are version control systems.
It helps you track changes in your files and work on different versions, and we can roll it back if required.
It remembers every change you make, who made it, when they made it, and why.
What are Git and GitHub?
GitHub is a website where you can store your Git projects online.
You can share code, work with Team, and keep a backup of your work.
GitHub is built on Git but offers more powerful features such as:
- Securely hosting your code online
- Easy teamwork without overwriting each other’s work
- Reviewing and approving changes before adding them to the main code (pull requests)
- Managing tasks, issues, and project progress in one place
- Sharing code publicly so others can use and contribute (open source)
Note: “Open source” means your code is free for anyone to see, use, and improve.
Git and GitHub How It Works
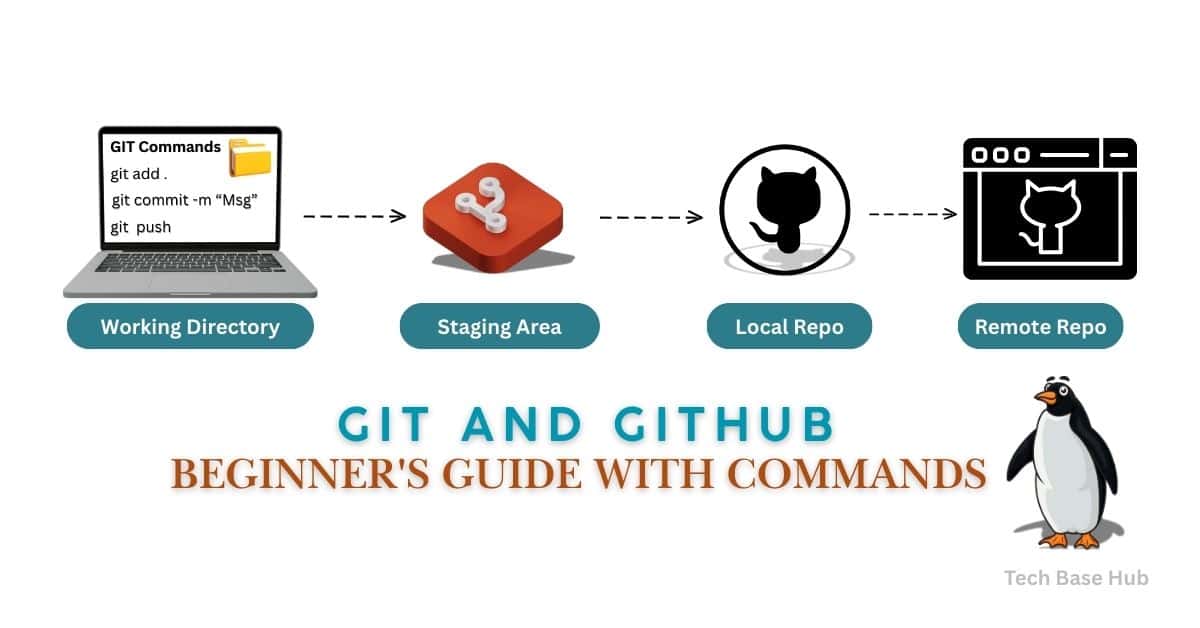
In Git, work moves through 4 main stages:
Working Directory → Staging Area → Local Repository → Remote Repository
Git and GitHub Workflow
| Stages | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Working Directory | Where you write/edit code (not yet tracked in Git). |
| Staging Area | Changes are ready to commit. |
| Local Repository | Your committed history is stored on your computer. |
| Remote Repository | Stored on GitHub or any remote server. |


ALSO READ:
- Zenity IT Asset Request Tool – The Ultimate Linux Automation (2025)
- Discover the Top 5 Differences Between Containers and VMs – Made Easy
- 1 Powerful Shell Script to Monitor Missing Mount Points in Linux
Click here to go to the GitHub repos link
Common Git and GitHub Commands (With Examples)
List of the most used Git commands and when to use them.
# 1. Clone a Repository Download a project from GitHub to your local machine.
git clone <url>
# 2. See Changes
git diff
# Shows changes between Working Directory ↔ Staging Area.
git diff HEAD
# Shows changes between Working Directory + Staging Area ↔ Last Commit.
git diff --staged # same as --cached
# Shows changes between Staging Area ↔ Last Commit.
git diff <commit-or-branch>
# Compares your current work with another commit/branch.
git diff --cached <commit-or-branch>
# 3. Moves changes from Working Directory → Staging Area.
git add <file>
git add . # add all files
# 4. Commit Changes
git commit -m "Message"
# Stages and commits all tracked files in one step (skips git add).
git commit -a -m "Message"
# 5. Push to Remote
git push origin main
# 6. Gets the latest changes from remote without merging them into your branch.
git fetch
# 7. Combines another branch’s changes into your current branch.
git merge
# 8. Fetch + Merge in one step (gets remote changes and merges them into your branch).
git pull
# 9. Shows commit history in detail.
git log
# Shows commit history in short form.
git log --oneline
# 10. Make a new branch and change to new branch
git checkout -b feature-branch