A Beginner’s Guide to Cloud Shell Commands and gcloud: GSP002 2024
Cloud Shell Commands and gcloud: GSP002 Cloud Shell provides command-line access to Google Cloud resources. Running on a Debian-based virtual machine with a 5-GB home directory, it comes pre-installed with the gcloud tool and other utilities, allowing you to start working quickly.
Cloud Shell Commands and gcloud: GSP002 Objectives :
- Practice using gcloud commands.
- Connect to compute services hosted on Google Cloud.
Cloud Shell Commands and gcloud: GSP002 Prerequisites:
- A Google Cloud account.
- Google Cloud SDK installed on your local machine.
- Basic knowledge of command-line operations.
ALSO READ:
- Google Cloud virtual machine GSP001: Creating a Virtual Machine 2024
- Swap Monitoring: Keep Your System Performance in Check
- Improve System Performance: Clear Linux Cache Easily Bash Script
Action Plan :
Step 1: Sign in to Google Cloud Platform
- Go to the Google Cloud Platform Console.
- Sign in with your Google account credentials.
Step 2: Activate Cloud Shell
Open Cloud Shell by clicking the terminal icon in the top-right corner of the console.
List the active account name (optional):
gcloud auth list
Click on Authorize.
To list the project ID:
gcloud config list project
Step 3: Configuring Your Environment
Set Region:
gcloud config set compute/region REGION
Set Zone:
gcloud config set compute/zone ZONE
View the project ID:
gcloud config get-value project
To view details about the project:
gcloud compute project-info describe --project $(gcloud config get-value project)
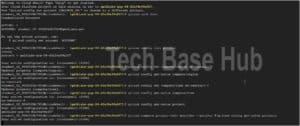
Set Environment Variables:
Create an environment variable to store your Project ID:
export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
Create an environment variable to store your Zone:
export ZONE=$(gcloud config get-value compute/zone)
To verify the variables:
echo -e "PROJECT ID: $PROJECT_ID\nZONE: $ZONE"
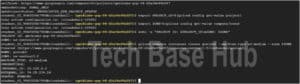
Step 4: Create a Virtual Machine
To create your Virtual Machine:
gcloud compute instances create gcelab2 --machine-type e2-medium --zone $ZONE
Step 5: Filtering Command-Line Output
List the compute instances available in the project:
gcloud compute instances list
List the gcelab2 virtual machine:
gcloud compute instances list --filter="name=('gcelab2')"
List the firewall rules for the default network:
gcloud compute firewall-rules list --filter="network='default'"
Step 6: Connecting to Your Virtual Machine
Connect to your virtual machine with SSH:
gcloud compute ssh gcelab2 --zone $ZONE
To continue, type Y.
Install Nginx Web Server:
sudo apt install -y nginx
Exit the SSH session:
exit
Step 7: Update Firewall Rule
Create a firewall rule to allow HTTP traffic:
gcloud compute firewall-rules create default-allow-http --direction=INGRESS --priority=1000 --network=default --action=ALLOW --rules=tcp:80 --source-ranges=0.0.0.0/0 --target-tags=http-server
List the firewall rules for the project:
gcloud compute firewall-rules list --filter=ALLOW:'80'
Step 8: Viewing the System Logs
List available logs:
gcloud logging logs list
List related compute resources:
gcloud logging logs list --filter="compute"

Testing Your Understanding
Three basic ways to interact with Google Cloud services and resources are:
Client libraries
Command-line interface
Cloud Console
We have completed the getting started with Cloud Shell Commands and gcloud: GSP002 2024